Unravelling Alpha-Mangostin as a Promising Anticancer Agent: An Overview of Therapeutic Effects, Molecular Mechanisms, and Strategies to Improve Treatment Outcomes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36877/pmmb.a0000474Abstract
Cancer represents a significant global health concern, contributing to a high number of fatalities in the 21st century, with projections indicating a continuous spike in cancer cases. Although chemotherapy is an established cancer treatment, it is often associated with adverse effects and chemoresistance. Thus, alternative therapies like natural products that can address these limitations of chemotherapy are crucial. Alpha-mangostin (AM), derived from the mangosteen fruit, has widely demonstrated potent anticancer and enhanced chemosensitivity properties by regulating oncogenic signaling pathways, including phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt), nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. This review discusses the current anticancer status of AM in preclinical studies and associated molecular mechanisms. It also further identifies the challenges and strategies to enhance the anticancer activity of AM. AM has shown strong anticancer effects in preclinical studies across multiple cancer types, including breast, cervical, ovarian, colorectal, pancreatic, prostate, and lung cancers. It induces apoptosis, causes cell cycle arrest, and inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells. AM also reduces cancer progression and metastasis by targeting key signaling pathways, demonstrating broad therapeutic potential. To overcome the limitations of AM, such as low bioavailability and limited clinical evidence, strategies like nanotechnology, chemical modification, and combination with chemotherapeutic agents have been proposed. These approaches aim to enhance AM's therapeutic potential. However, further research is needed to assess its pharmacokinetics, safety, and clinical efficacy. Future studies should also focus on improving delivery systems and conducting rigorous clinical trials to support AM’s use in integrative cancer therapy.
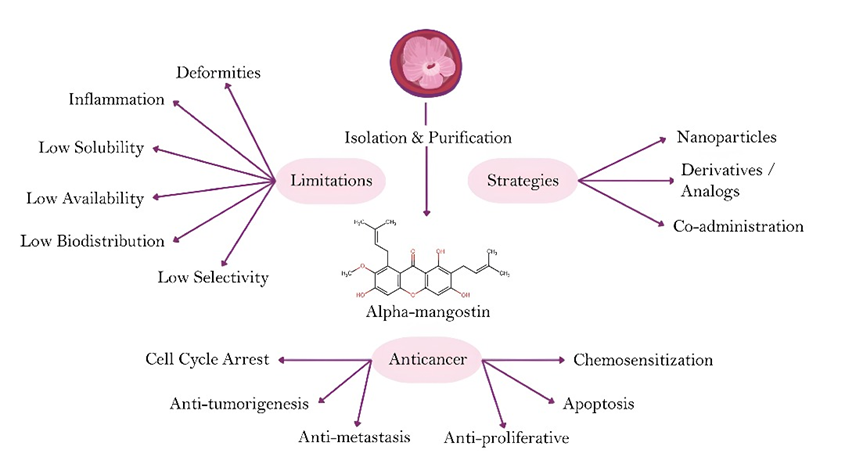
Graphical abstract. Alpha-mangostin exerts anticancer effects by regulating cell cycle arrest, inhibiting tumorigenesis, metastasis, and cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, and enhancing chemosensitivity. However, its therapeutic potential is limited by low solubility, bioavailability, and biodistribution, which could be improved through nanoparticle encapsulation, derivative synthesis, or combination with other chemotherapeutic agents.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yuan Seng Wu, Xinwei Koong, Thin Zar Soe, Jieen Low, Wi Xin Tan, Megan Kee Ern, Alishbah Amir, Yan Li Wong, Michelle Felicia Lee, Maverick Fook Choy Yap, Long Chiau Ming

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Author(s) shall retain the copyright of their work and grant the Journal/Publisher right for the first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under:
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0). This license allows for the copying, distribution and transmission of the work, provided the correct attribution of the original creator is stated. Adaptation and remixing are also permitted.

This broad license intends to facilitate free access to, as well as the unrestricted reuse of, original works of all types for non-commercial purposes.
The author(s) permits HH Publisher to publish this article that has not been submitted elsewhere.


.png)

.jpg)
