A Current Overview of Next-Generation Probiotics and Their Prospects in Health and Disease Management
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36877/pmmb.a0000457Abstract
Traditional probiotics have been extensively studied, and their effectiveness in gut modulation is well established. However, emerging research has shifted focus to previously understudied probiotic strains, now known as next-generation probiotics (NGPs), with the aim of harnessing their unique potential to elicit targeted therapeutic effects in disease management. This study aims to provide a comprehensive review on the recent evidence on NGPs by exploring their potential roles and applications in human health and agricultural settings. The literature search was conducted systematically across four databases with the keywords “next generation probiotics” and “gut health” or treatment” or “therapy”. The findings of this review identified promising NGPs, including Akkermansia muciniphila, Bacillus sp., Bacteroides sp., Enterococcus sp., Faecalibacterium sp., Parabacteroides sp., and Streptomyces sp. These NGPs can elicit targeted effects in specific disease states while simultaneously restore gut dysbiosis by promoting beneficial bacteria, elevated short-chain fatty acid levels, and stimulate immunomodulatory effects to reduce inflammation. These modes of action are closely linked to one another, acting as a positive feedback loop to reduce inflammation in the host. Besides, other niche NGPs that are lesser-studied also show therapeutic effects in disease management, highlighting the importance of further research into these species to uncover potential mechanistic pathways for treating various illnesses. In summary, NGPs can offer targeted therapeutic effects in addition to probiotic effects in the gut, providing a multi-faceted approach in treating various health conditions. The development of therapeutics with these NGPs could offer alternatives to current treatment strategies to improve disease outcomes and prognosis. Nevertheless, future research is essential to better elucidate the exact mechanisms, safety profiles, and therapeutic applications of these NGPs.
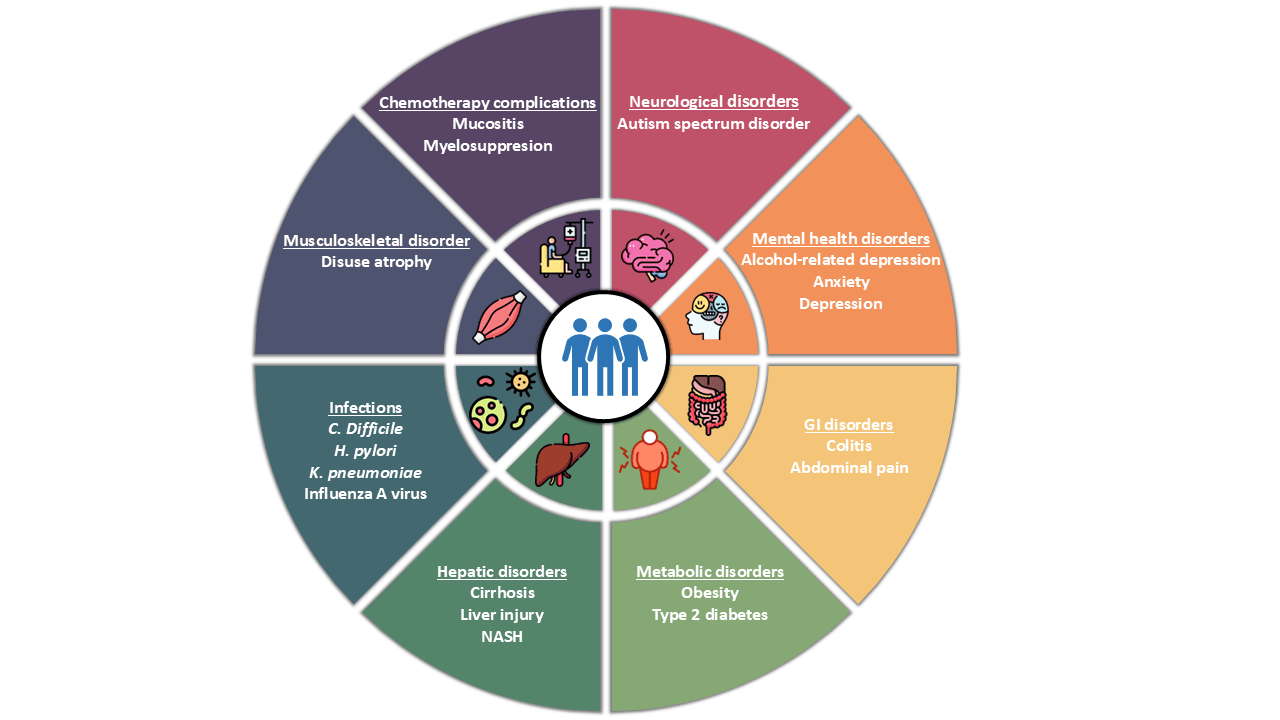
Graphical abstract: The potential therapeutic applications of NGPs.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Ke-Yan Loo, Joanne Yuen Heng Thong, Loh Teng-Hern Tan, Vengadesh Letchumanan, Kok-Gan Chan, Learn-Han Lee, Jodi Woan-Fei Law

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Author(s) shall retain the copyright of their work and grant the Journal/Publisher right for the first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under:
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0). This license allows for the copying, distribution and transmission of the work, provided the correct attribution of the original creator is stated. Adaptation and remixing are also permitted.

This broad license intends to facilitate free access to, as well as the unrestricted reuse of, original works of all types for non-commercial purposes.
The author(s) permits HH Publisher to publish this article that has not been submitted elsewhere.


.png)

.jpg)
